Electrical wiring powers our homes, workplaces, and industries. Every flick of a light switch, device charging, or machine operation depends on a network of wires. However, the choice of wire is about maintaining safety, optimizing performance, and adhering to regulatory standards. At Sonic Electric, we deliver top-quality wires and cables that cater to diverse applications with reliability.
Choosing the right electrical wire types and uses can distinguish between a system that runs efficiently and one prone to hazards. With the myriad of wires available, understanding their applications and properties is important for any project. Let’s explore the fundamentals and examine the different wire types and uses.
The Core of Electrical Wire Types and Uses
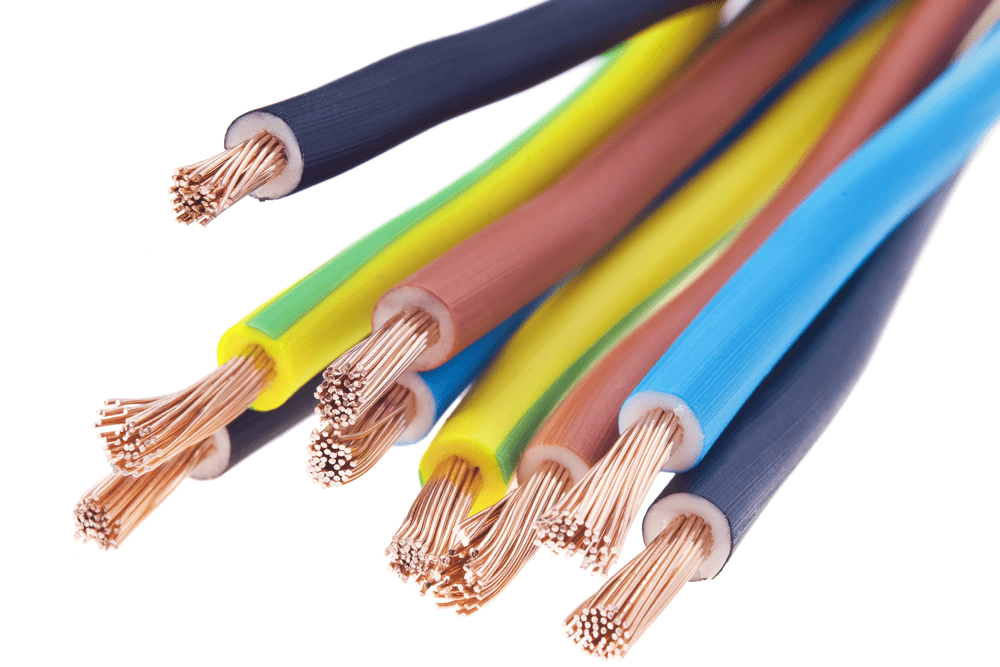
Electrical wires serve as conduits for electricity, transmitting power or signals from one point to another. Conductors such as copper and aluminum are widely used due to their excellent electrical properties. Insulation materials protect these conductors from environmental damage and guarantee safety. The type of wire chosen directly influences the system’s performance, cost, and longevity.
Copper wire remains the industry standard for its reliable conductivity and durability. It minimizes energy loss, making it ideal for applications where efficiency is needed. Aluminum wire offers a cost-effective alternative. It is particularly used for large-scale installations, where its lightweight nature eases handling and reduces structural strain.
Additionally, specialized wires like Nichrome or tinned copper serve specific purposes such as heating elements and corrosion-resistant marine systems.
Each wire type addresses challenges, from withstanding extreme temperatures to resisting environmental degradation. Selecting the correct wire for an application involves understanding its conductivity, mechanical strength, and compatibility with the operating environment.
Exploring Electrical Cable Types
While wires are individual conductors, electrical cables bundle them together for added protection, organization, and easier installation. These electrical cable types cater to various environments, demands, and applications. From household wiring to industrial systems, each cable type is designed to optimize performance and safety. Below, we explore ten common types of electrical cables and their uses.
Nonmetallic (NM) Cable
Nonmetallic cable or NM cable, is widely recognized for its versatility and simplicity in home electrical systems. Its protective plastic sheath safeguards the individual conductors from physical damage. It also provides insulation against electrical currents.
This cable type is especially useful for indoor wiring projects such as connecting outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. The flattened, tubular design of NM cable makes it easy to pull through walls, ceilings, and floors. Its affordability and reliability make it the go-to choice for residential applications. However, due to its lack of moisture resistance, it’s limited to dry, interior locations.
Underground Feeder (UF) Cable
Underground Feeder cable stands out for its rugged construction. They are designed to endure harsh outdoor conditions. Unlike NM cable, the solid plastic sheath of UF cable provides a watertight seal. This prevents moisture from penetrating and damaging the conductors.
This cable is suitable for direct burial without the need for additional protection. UF cable powers outdoor lighting, irrigation systems, or detached structures like garages or sheds. Its durability and resistance to environmental factors present reliable performance in outdoor and underground installations.
THHN and THWN Wires
THHN and THWN wires are staples for industrial and commercial applications. They offer exceptional heat and moisture resistance. The thermoplastic insulation allows these wires to handle high temperatures, while the nylon coating protects against abrasion and chemicals.
THWN wires are specially designed for wet environments. When housed in conduit, they are suitable for outdoor installations. These wires are ideal for short, exposed runs or use within conduit systems in areas like basements, garages, or industrial facilities. Their versatility and durability make them a preferred choice for electricians tackling challenging environments.
Shielded Cable
Shielded cable provides a solution for environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) poses a problem. The foil or braided shield within the cable absorbs and deflects external electrical noise. Hence, it can protect the integrity of the signals carried by the internal conductors.
This feature is necessary for sensitive applications. Examples are such as audio recording studios, industrial automation, or medical equipment. In these applications, even minor disruptions can cause significant issues. Shielded cables also help prevent signal cross-talk in data transmission systems. They guarantee clear and reliable communication between devices.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cables are a mainstay in the telecommunications and broadcasting industries due to their efficient signal transmission capabilities. Their layered design includes a central conductor and protective layers. This helps reduce signal loss and block interference.
Coaxial cable are a reliable choice for television, cable internet, and satellite connections. Although newer technologies like fiber optics are gaining traction, coaxial cables remain a trusted solution for many residential and commercial applications.
Ethernet Cable
Ethernet cables have become indispensable in modern networking. They can connect everything from personal computers to office networks. The twisted-pair design of Cat 5 and Cat 6 cables minimizes electromagnetic interference and supports high-speed data transmission.
These cables are commonly used in local area networks (LANs). They provide the backbone for internet connectivity and data sharing. Ethernet cables are particularly valued for their ability to efficiently handle large amounts of data. Their flexibility and scalability make them an important component of digital infrastructure.
Low-Voltage Cable
Low-voltage cables are specifically made for systems operating below 50 volts. They are ideal for applications that don’t require high power. They are commonly used in landscape lighting, doorbells, intercoms, and automation systems like smart thermostats or sprinkler controls.
These cables are lightweight and easy to install. They often come bundled in flexible sheathing for added convenience. Their small size and low current capacity make them safe for non-hazardous applications. On the other hand, their versatility allows them to adapt to various residential and commercial needs. Low-voltage cables are key components in modern automation and energy-efficient solutions.
Ribbon Cable
Ribbon cables are characterized by their flat, ribbon-like design which organizes multiple conductors in parallel. This unique shape allows them to fit into tight spaces. Hence, they are ideal for use in electronic devices like computers, printers, and appliances.
Each conductor is individually insulated to deliver precise signal transmission without interference. Ribbon cables are particularly useful in devices with limited space, where traditional round cables might be too bulky. Their neat, orderly arrangement simplifies troubleshooting and repairs. It’s a favorite among manufacturers and technicians working with compact electronics.
Armored Cable
The armored cable comes with a sturdy metal sheath. They are made to protect electrical conductors from physical damage. This makes it popular for exposed installations in garages, workshops, and industrial settings. These are settings where wires may be at risk from tools, machinery, or heavy traffic.
The metal jacket provides both mechanical protection and a degree of shielding from electromagnetic interference. Armored cables are also fire-resistant, adding an extra layer of safety in high-risk environments. Their ability to be installed without conduit simplifies installation while maintaining durability and compliance with building codes.
Metal-Clad (MC) Cable
Metal-clad (MC) cable shares many features with armored cable but offers enhanced versatility and protection. It includes a full-sized ground wire, which presents reliable grounding even in demanding applications. The internal conductors are insulated with plastic to protect against moisture and abrasion.
MC cables are approved for damp locations when fitted with an outer PVC jacket. They are suitable for outdoor use or installations in harsh environments. Their construction makes them a preferred choice for industrial facilities and outdoor installations where durability is necessary.
These electrical cable types highlight the diversity and specialization within the world of wiring. Each type is engineered to meet the demands of modern electrical systems. They are for safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability across residential, commercial, and industrial projects.
Applications of Electrical Wire Types
Electrical wires are versatile because they can meet various industry and environmental challenges. Each type of wire is engineered to address different demands. Understanding these applications highlights the importance of proper wire selection and its impact on modern systems.
Copper Wire in Building Wiring
Copper wire remains the gold standard for residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations. Its superior conductivity delivers efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss.
Copper’s ability to resist overheating adds a layer of safety. It reduces the risk of electrical fires. This is why most building codes recommend or require copper wiring for compliance with safety standards. Its flexibility and durability make it suitable for wiring everything from lighting fixtures to heavy machinery.
Aluminum Wire in Power Transmission
Aluminum wire is the foundation of power transmission networks. Long distances and large-scale installations demand lightweight yet efficient materials, making it an ideal choice. Its reduced weight minimizes structural strain on towers and supports.
Aluminum’s cost-effectiveness further solidifies its role in substations and distribution systems. It helps provide a reliable flow of electricity from power plants to homes and businesses. While slightly less conductive than copper, aluminum compensates with its affordability and compatibility with advanced power technologies. It enables scalable solutions for modern energy infrastructure.
Steel Wire in Structural Applications
Steel wire excels in structural applications where strength and durability are non-negotiable. In the construction industry, it reinforces concrete structures and offers tensile strength that prevents cracking and failure under stress. Steel wire supports suspension bridges and high-rise buildings, where reliability is key.
Beyond construction, steel wire is a trusted material for security fencing and tensioning systems. It offers resilience against environmental wear and physical impact. Its longevity and reliability make it indispensable for projects that demand long-term structural integrity.
Nichrome Wire in Heating Systems
Nichrome wires are made from a nickel-chromium alloy. It is a workhorse in heating systems and industrial furnaces. It can withstand extreme temperatures without oxidizing or degrading. This makes it perfect for applications that require consistent and reliable heat generation.
Nichrome wire is commonly used in appliances like toasters, ovens, and hair dryers. It powers furnaces and kilns in industrial settings to deliver predictable performance over extended periods. Its high resistance and heat stability maintain energy efficiency and safety in these demanding environments.
Tinned Copper Wire in Corrosive Environments
Tinned copper wire is the go-to solution for harsh environments where moisture, salt, and corrosive elements pose a threat. The tin coating provides additional protection against oxidation. It presents long-term reliability in marine vessels, automotive systems, and industrial machinery.
In marine applications, tinned copper resists the corrosive effects of saltwater. It helps maintain conductivity and prevent system failures. Additionally, its ease of soldering makes it a favorite for creating secure connections in automotive wiring harnesses. Tinned copper wire offers safety and durability where standard copper might fail.
Key Factors in Choosing the Right Wire
Selecting the right wire is a decision that directly impacts any electrical system's performance, safety, and longevity. Conductivity, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance all play a role in wire selection.
Conductivity and Application Requirements
Conductivity is one of the most important factors when selecting a wire. With its exceptional conductivity, copper is the top choice for energy-intensive applications. It allows electricity to flow efficiently with minimal energy loss. Hence, it is ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial systems where reliability is key.
While not as conductive as copper, aluminum offers a lightweight and cost-effective alternative. It is commonly used in large-scale power distribution systems where weight reduction and affordability are important. Nichrome wire provides high resistance to efficiently convert electrical energy into heat for applications like heating elements.
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which a wire will be used greatly influences its selection. High-temperature environments require wires like Nichrome, which can withstand extreme heat without degrading. In marine or automotive applications, tinned copper wire is preferred for its corrosion resistance.
Outdoor applications often require UV-resistant or armored cables to protect against sunlight, water, and physical damage. Underground installations demand durable solutions like Underground Feeder (UF) cables to endure moisture and direct burial conditions. Matching the wire to the environment helps with its longevity and reliable performance.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to regulatory standards is non-negotiable when selecting electrical wires. Local and international codes establish minimum materials, insulation, and design requirements for safety. For example, building codes often specify copper wire for indoor residential wiring due to its safety record and compatibility with code requirements.
Comply with these standards to avoid accidents, legal liabilities, and expensive system failures. Consulting with licensed professionals can help manage these regulations and select wires that are both compliant and fit for purpose.
Longevity and Maintenance
Durability and maintenance requirements are also considerations. Wires exposed to harsh environments or physical stress must be designed to resist wear and tear. Selecting the right wire type reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. For example, tinned copper wire offers corrosion resistance in demanding conditions. In applications where wires are subject to movement or vibration, stranded wires are often used due to their flexibility and ability to withstand mechanical stress.
The Importance of Specialized Wire Types
Specialized wires address unique challenges that general-purpose wires cannot. They offer specialized solutions for specific applications. They are central in modern electrical systems, where standard wires might fail to deliver the required performance, safety, or durability.
Specialized wires guarantee reliable operation in demanding environments by offering targeted functionalities such as interference reduction, heat resistance, or corrosion prevention.
Twisted Pair Cables for Telecommunications
Twisted pair cables are indispensable in the telecommunications industry because they minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI). These cables create a balanced signal path that reduces external noise and crosstalk between neighboring wires. It does so by twisting two insulated conductors together.
This feature is important for maintaining clear and reliable data transmission in telephone lines, internet connections, and local area networks (LANs). Twisted pair cables are also used in high-speed Ethernet networks, where signal integrity is necessary for performance.
Shielded Wires for Sensitive Electronics
Shielded wires provide valuable protection in environments where electrical noise could disrupt sensitive systems. The additional layer of shielding is made from foil or braided wire. It absorbs and deflects external interference, safeguarding the integrity of the signals carried by the internal conductors.
These wires are crucial in medical equipment, audio systems, and industrial automation. Even minor disruptions could lead to inaccuracies or equipment failure. Shielded wires also help in environments with high EMI, such as factories with heavy machinery or control rooms filled with electronic devices.
Specialized wires show the importance of matching wire types to specific applications. They enable efficient performance in environments where standard options might fail. Reducing interference in communication systems, generating heat in industrial furnaces, or resisting corrosion in marine environments show how these wires meet modern electrical demands. Understanding and using specialized wires helps professionals create efficient systems tailored to their needs.
Sonic Electric: Your Partner in Electrical Wiring
At Sonic Electric, our collection offers a broad range of products to meet the highest safety and performance standards. Our solutions cater to all requirements, from durable copper wires for residential applications to reliable metal-clad cables for industrial use.
We also provide Orbit Industries electrical supplies that complement our wires and cables for long-term reliability. Our expertise and commitment to quality make us a trusted partner for professionals across industries. Explore our electrical cables and wires collection today and power your projects confidently.






Share:
Metallic Vs. Non-Metallic Conduit: A Comparison Guide
What Is Liquid Tight Conduit? Applications And Uses